Link
ENVIRONMENT
FDJ is taking action for the climate and to promote biodiversity

CLIMATE
Reduce our impact on the environment and tackle climate change
FDJ Group is committed to reducing its impact on the environment. In practice, this means reducing the direct and indirect carbon emissions that our business activities generate.
Measure FDJ’s greenhouse gas emissions
We have been measuring our carbon output since 2008 to track greenhouse gas emissions that our business activities generate and fine-tune our reduction strategies.
To ensure alignment with the Group’s targets, greenhouse gas emission tracking became annual in 2017 using the GHG Protocol methodology.
Our carbon footprint measurements take into account emissions from scopes 1, 2, and 3:
- Scope 1: direct greenhouse gas emissions linked to combustion for air conditioning and the company’s fleet of vehicles.
- Scope 2: indirect greenhouse gas emissions linked to electricity use and heating and cooling systems.
- Scope 3: other indirect greenhouse gas emissions associated with purchasing goods and services, freight, fixed assets (properties, furniture and equipment, and IT stock) and waste.
FDJ Group’s business activities are categorised into carbon emissions using the GHG Protocol methodology.
| Scope | 2022 carbon emissions (TCO2e) |
| Scope 1 | 1,567 |
| Scope 2 | 5 |
| Scope 3 | 108,074 |
Reduce FDJ’s carbon emissions
In 2019, we decided to set a roadmap to reduce our carbon footprint through four main targets leading up to 2025. The project was validated by the international initiative Science Based Targets (SBT).
Having already met these targets, FDJ has now laid out a new roadmap to take us to 2030, this time with a target rise in temperatures of no more than 1.5 °C, to align with the expectations of the Paris Agreement.
The Science Based Targets initiative
The Science Based Targets initiative was rolled out internationally in 2015, following COP21. Its goal is to support businesses in defining carbon reduction roadmaps that meet the targets of the Paris Agreement and are based on current scientific understandings.
Energy saving at FDJ
In 2022, FDJ implemented an energy saving plan that called for tangible and practical action. Our target is to reduce energy consumption across all the Group’s sites in France. This plan also contributes to the national energy saving plan set out by the French government.
-

Reducing the energy consumption of buildings
By adjusting the indoor temperature and optimising lighting systems.
-
Reducing energy consumption relating to digital technologies,
By adjusting cooling temperatures in IT rooms and deploying digital eco-actions
-

Reducing energy consumption linked to travel,
By scaling back work-related travel, adapting modes of travel and speeding up the switch to an all-electric fleet of company vehicles.
Develop a responsible digital strategy
FDJ is committed to its continuous improvement strategy when it comes to the environmental and social impact that its digital activities have.
FDJ partnered with WWF France in 2019 to participate in the WeGreenIT study. This strategy enabled us to assess the impact of our IT equipment and define an action plan for reducing it. Several initiatives were rolled out:
In our data centres:
- Energy efficiency improvements,
- Increase in density of physical servers.
Employee IT devices:
- Increase life span of devices,
- Repair rather than replace,
- Buy “TCO Certified” equipment.
BIODIVERSITY
FDJ is taking action to protect biodiversity
Alongside putting our commitment to tackling climate change into action, FDJ Group is also actively contributing to protecting biodiversity to limit the impact our games have on forest biodiversity.
Paper is made from trees, which is a priority resource in FDJ’s business activities for producing and distributing our games. For over 10 years, we have actively participated in taking care of our forests and protecting them, in France and around the world.
Reduce FDJ’s impact on biodiversity
100% of our paper games are printed on FSC® certified paper
Since 2012, 100% of our paper games have been printed on responsibly-sourced, FSC® certified paper (licence number: FSC®-N002595).
FSC® is an organisation that protects forests around the world. It promotes a wide variety of species, protecting soils and local flora and fauna. It is also instrumental in tackling rainforest destruction.
FSC® certification is a fundamental tool in the protection of forest ecosystems, which are threatened by intensive exploitation.
Analysis of the biodiversity footprint of our paper games
In 2020, FDJ carried out a lifecycle analysis of its paper games. The aim was to measure the impact they had on the environment and on biodiversity. Our paper games’ biodiversity footprint was measured using the Global Biodiversity Score (GBS), developed by CDC Biodiversité (part of the Caisse des Dépôts group).
Partnership with the Gestes Propres organisation
In 2022, FDJ began a partnership with Gestes Propres (Clean Living), a pioneer organisation in the fight against littering. We amplified the “Small Waste” campaign to raise awareness among the general public and our clients about the importance of throwing small waste in the bin, especially scratch cards.
The film was shown in 23,000 FDJ points of sale with digital screens in 2022 and 2023, as well as on social media. It was another way to limit the impact that small pieces of rubbish can have on the environment and local biodiversity.
Support biodiversity protection projects
Since 2019, FDJ has been committed to protecting biodiversity in France’s forests. Every year, we finance “Ecosystem FSC Biodiversity Services” projects that contribute to protecting not only the forests but ecosystem services, too, while generating economic benefits for forest owners.
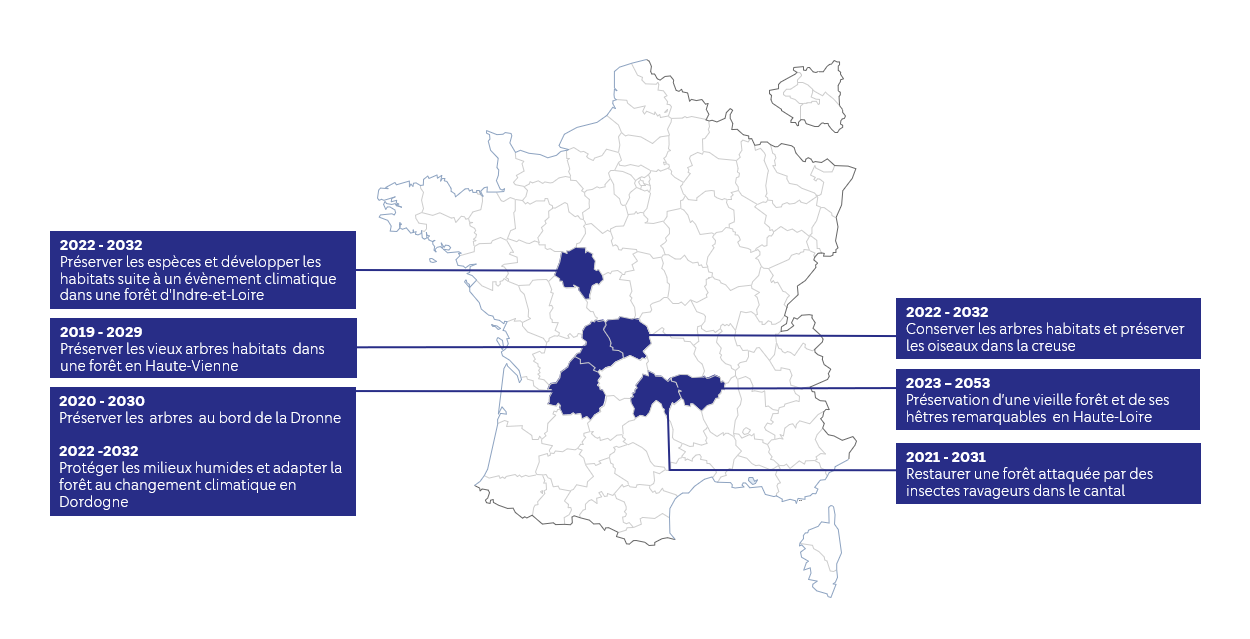
FDJ sponsors several funds for restoring biodiversity
-

ONF – Fonds Agir pour la forêt (Take Action for the Forest)
In the wake of the devastating forest fires that ravaged French forests during the summer, FDJ Group donated €200,000 to the ONF (National Forestry Office) fund to contribute towards a national effort to build back the damaged ecosystems.
The money will be split up and used in two ways:
- 80% will go towards rebuilding the public forests in the Gironde region.
- The remaining 20 % will be used to rebuild public forests in Britanny, the Loire Valley, and Poitou-Charentes.
-

WWF – Nature Impact
FDJ sponsors the Nature Impact fund launched by WWF France, the first fund to be based on the Payments for Ecosystem Services (PSE) framework, and which serves the double purpose of protecting biodiversity and capturing carbon emissions.
The initiative’s main target is the conservation and restoration of biodiversity, the first ambitious target being the conservation of around 15,000 hectares of the most threatened forests. Protecting these hectares of land will contribute to a slowdown in climate change and have a positive impact on the climate through capturing and storing 400,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide over 30 years.
FDJ’s biodiversity strategy between now and 2030
In 2022, we defined a new biodiversity 2030 strategy, based on four pillars:
- Reduce the impact of our games on biodiversity
- Contribute to the protection of biodiversity in the countries we operate in
- Raise awareness among our customers and wider public
- Share best practices to inspire other industry players
Recyclable paper games!
FDJ’s scratch cards, lottery tickets, and paper receipts are all 100% recyclable. They need to be correctly recycled to enjoy a second life.
